Understanding the Environmental Impact of Die Casting Mold and Plastic Mold
The industrial processes of die casting Mold and plastic mold are integral to modern manufacturing, producing essential components for a myriad of products.However, as businesses keep on developing, so does the attention on their natural effect. Understanding what these cycles mean for the climate is urgent for organizations hoping to embrace economical practices and for purchasers settling on informed decisions.
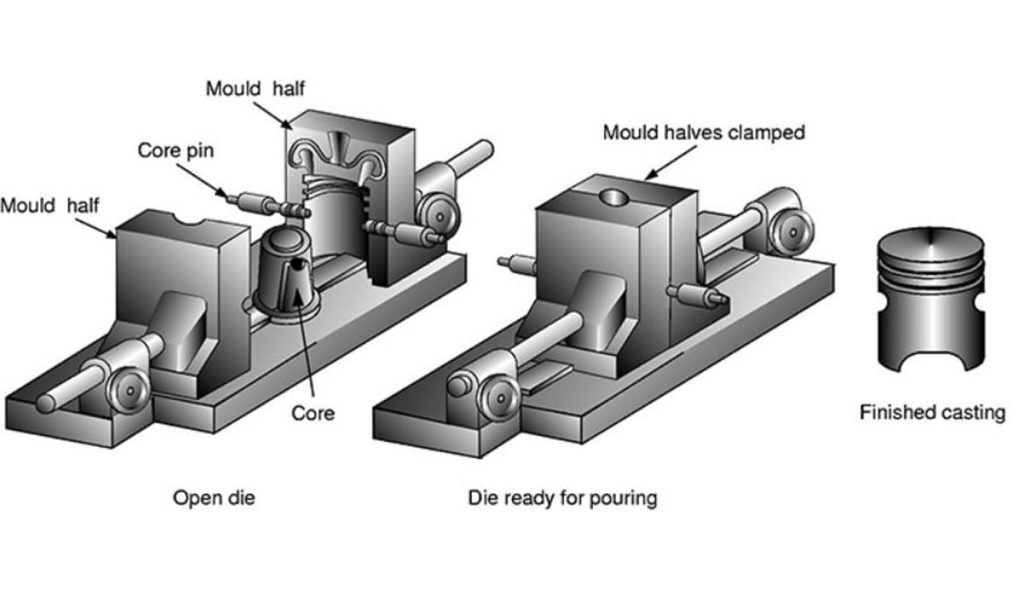
The Fundamentals of Die Casting
Die casting is an assembling interaction where liquid metal is infused into a steel form or kick the bucket under high tension. This technique is regularly used to deliver metal parts with multifaceted shapes and is leaned toward for its high creation productivity and the capacity to make complex calculations.
Materials Used in Die Casting
Die casting Mold basically includes metals like aluminum, zinc, magnesium, and copper. Every one of these metals has unmistakable properties that make them reasonable for various applications. Aluminum, for example, is lightweight and erosion safe, making it ideal for auto and aviation parts. In any case, the extraction and handling of these metals, especially aluminum, are energy-escalated, contributing altogether to ozone harming substance discharges.
Environmental Concerns in Die Casting
One of the essential natural worries related with Die casting Mold is the high energy utilization expected to soften and infuse the metal into molds. This energy frequently comes from non-sustainable sources, prompting expanded fossil fuel byproducts. Moreover, the cycle produces modern waste, including metal pieces and utilized molds, which can be trying to reuse or discard reasonably.
The utilization of coolants and ointments in Die casting Mold likewise presents natural dangers. These substances can be destructive while possibly not appropriately made due, possibly defiling soil and water sources. In addition, the outflow of unstable natural mixtures (VOCs) during the cycle can add to air contamination, presenting wellbeing dangers to laborers and close by networks.
The Process of Plastic Molding
Plastic molding, then again, includes molding plastic materials into wanted structures by applying intensity and tension. This interaction is adaptable and used to make everything from family things to clinical gadgets.
Types of Plastic Molding
A few techniques for plastic trim exist, each with its own natural ramifications:
- Infusion Trim: The most widely recognized structure, where liquid plastic is infused into a form. While exceptionally proficient, it requires critical energy, and the development of plastics depends vigorously on petroleum derivatives.
- Blow Trim: Utilized for making empty plastic items like jugs. This cycle likewise consumes a lot of energy and frequently prompts squander as overabundance material that should be managed.
- Rotational Trim: Includes turning a form while warming plastic material. However it considers the formation of huge, empty articles, it is less productive and creates more waste contrasted with different strategies.
Environmental Concerns in Plastic Mold
The ecological effect of plastic Mold is fundamentally determined by the extraction and handling of unrefined substances. Most plastics are gotten from oil, a non-sustainable asset, and the creation cycle is energy-concentrated, adding to ozone harming substance discharges.
Plastic waste is another critical concern. While a few plastic items are recyclable, many end up in landfills or the sea, where they can require many years to disintegrate. The presence of microplastics in the climate, coming about because of the breakdown of plastic waste, represents an extreme danger to marine life and possibly human wellbeing.
Besides, the creation of plastics frequently includes the utilization of substance added substances, for example, plasticizers and stabilizers, which can drain into the climate, causing soil and water pollution. The arrival of harmful outflows during the assembling system further worsens the ecological effect of plastic Mold.
Comparing the Environmental Impact
While contrasting the ecological effect of kick the bucket projecting and plastic trim, a few elements become an integral factor:
Energy Utilization
Kick the bucket projecting by and large requires more energy than plastic trim because of the great temperatures expected to liquefy metals. In any case, the kind of energy utilized (sustainable versus non-sustainable) can altogether impact the generally speaking ecological effect.
Material Manageability
Metals utilized in kick the bucket projecting are much of the time more recyclable than plastics, which can lessen the ecological impression. In any case, the underlying extraction of metals is more ecologically disastrous than the development of plastics.
Squander The board
The two cycles produce squander, however the idea of the waste contrasts. Pass on projecting waste essentially comprises of metal pieces, which are for the most part recyclable, though plastic trim waste frequently winds up as non-recyclable plastic waste, adding to long haul natural contamination.
Discharges and Contamination
Plastic trim is by and large connected with higher outflows of ozone harming substances and poisonous synthetics. Conversely, die casting Mold is more connected with metal waste and the potential for soil and water pollution because of the utilization of coolants and ointments.
Steps Toward Sustainability
While contrasting the ecological effect of kick the bucket projecting and plastic trim, a few elements become an integral factor:
Energy Utilization
Kick the bucket projecting by and large requires more energy than plastic trim because of the great temperatures expected to liquefy metals. In any case, the kind of energy utilized (sustainable versus non-sustainable) can altogether impact the generally speaking ecological effect.
Material Manageability
Metals utilized in kick the bucket projecting are much of the time more recyclable than plastics, which can lessen the ecological impression. In any case, the underlying extraction of metals is more ecologically disastrous than the development of plastics.
Squander The board
The two cycles produce squander, however the idea of the waste contrasts. Pass on projecting waste essentially comprises of metal pieces, which are for the most part recyclable, though plastic trim waste frequently winds up as non-recyclable plastic waste, adding to long haul natural contamination.
Discharges and Contamination
Plastic trim is by and large connected with higher outflows of ozone harming substances and poisonous synthetics. Conversely, die casting Mold is more connected with metal waste and the potential for soil and water pollution because of the utilization of coolants and ointments.
Conclusion
The environmental impact of die casting Mold and plastic mold is huge, however with continuous headways and a guarantee to manageability, the two enterprises can lessen their natural impression. By zeroing in on energy proficiency, squander decrease, and cleaner creation processes, makers can assume a vital part in safeguarding the climate while proceeding to fulfill the needs of present day culture.


